Semantics of Words
Notes
each word has two types of connections that together form the context by which we analyze the word, or derive the meaning from it:
- Chronic - all the past meaning of that word up to this point Intertemporal Identity
- Diachronic - all the words related to that point Interpersonal Identity together, this brings us to understand that language is an never-ending web of meaning Coherentism. Each word would lead us to another one. Same way you can't understand basketball without understanding games, balls, rules, the concept of teams, etc...
Language is not only a medium for delivering information, but rather the source itself of that information. Similar to the saying that writing is not the expression of thought but rather the act of creating those, the same with language. By being immersed in this tool that enables but also forces us to think in matter of meaning of symbols, the act of using them becomes also the act of creating meaning.
This means that it is very difficult to research a language from a static stable standpoint, like how modern computers "try" to understand language by coding it and it's connection to other words. Since the meaning of words and it's uses change over time, any language analysis is likely to suffer from Data Drift (article)
Visual
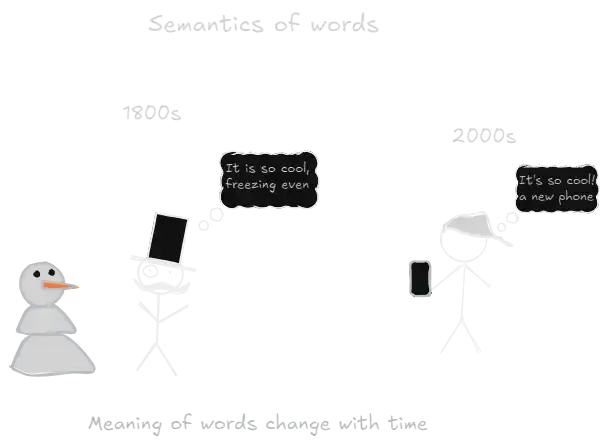
Overview
🔼Topic:: Philosophy of Language (Map) 🔼Topic:: NLP (Map) Source:: Philosophize This! Source:: Jacques Derrida Link:: https://share.snipd.com/episode/3e9990bc-d918-4fc6-afcd-ae8a9c2c5cec