Creativity Inc (book)
🔗Connect
🔼Topic:: Creativity (Map) 🔼Topic:: Team Management (Map)
✒️ Note-Making
💡Clarify
🔈 Summary of main ideas
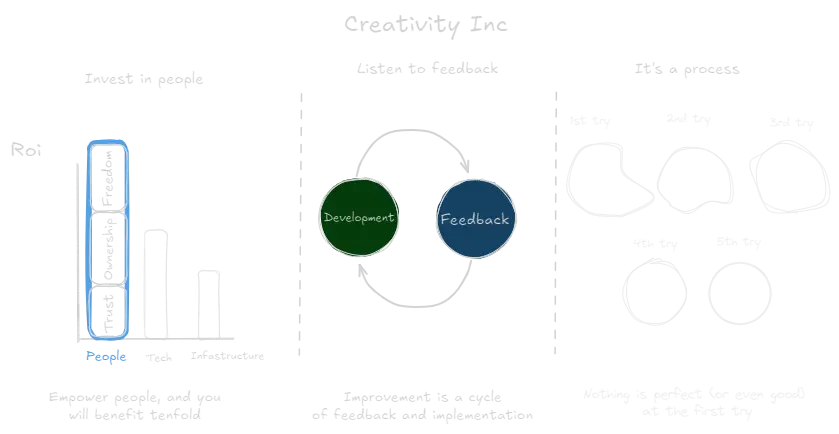
- Put people first - invest in their development and fulfilling their potential. When you give your employees a stake in the company and in the decision making, they will become the best they can be.
- Build trust - authenticity, transparency, and setting an example are key to build trust within and across hierarchy.
- Don't micro-manage - let people find their own solutions. When you intervene too much, you stifle creativity, responsibility and proactivity. Instead focus on helping them identify and understand the problems they face.
- Feedback circles - honest yet compassionate feedback, share and explore world views and perspectives with a group of peers, with no hierarchy, just the shared vision of creating something beautiful together.
- Proactivity is key - don't wait for problems to happen, look for them. Either intentionally or by chance, you might miss them if you trust that problems would resurface.
- Creativity is a process - nothing is perfect from the start, and not even good. It takes many iterations to distill a good idea.
🗒️Relate
⛓ Life lessons, action items
🔍Critique
✅ by following this method, what will happen? If done correctly, perhaps you will have the chance of managing people without crushing their innate creativity and will to contribute, and if you're a good manager, you might even succeed at helping them fulfill their potential.
❌ the logical jumps, holes or simply cases where it is wrong...
🧱 Implementations and limitations of it are... What if you are a small manager facing pressures and limitations from upper management? How could you implement the tips from this book?
🗨️Review
💭 my opinions on the book, the writers style... The stories within the book are captivating, even though some of them are highly technical and aren't really related to the story of creativity, but rather the specific context of pixar at the time. Since this is a "story first" kind of book, the structure of it is a bit messy, like trying to catch two birds with one stone. The "lessons" are distributed between the chapters and are hidden within the stories, only to be later displayed in a future chapter that feels unconnected to the rest of the book.
🖼️Outline
📒 Notes
Intro
managers should assume that:
- Workers are creative, motivated, and care about non-monitary aspects. They want to contribute humans are good as default
- Managing can hurt creativity
- Mistakes will be made, and need to explore, analyze and test solutions
- we will always have problems, many of them hidden from our view; that we work hard to uncover these problems, even if doing so means making ourselves uncomfortable; and that, when we come across a problem, we marshal all of our energies to solve it. (Location 135)
- We start from the presumption that our people are talented and want to contribute. We accept that, without meaning to, our company is stifling that talent in myriad unseen ways. Finally, we try to identify those impediments and fix them. (Location 213)
- managers must loosen the controls, not tighten them. They must accept risk; they must trust the people they work with and strive to clear the path for them; and always, they must pay attention to and engage with anything that creates fear. Moreover, successful leaders embrace the reality that their models may be wrong or incomplete. Only when we admit what we don’t know can we ever hope to learn it. (Location 223)
Part 1 - Getting Started
Chapter 1 - Animated
Three critical aspects of creativity:
- No hierarchy - discussions must be inclusive Psychological safety, ideas flowing freely up, down and across teams. Note that the environment can be influential. For example, a long table where the "important" people sit in the middle can silence those who sit on the edge Environmental design
- Trust - Micro-Management hurts creativity and motivation. Workers should feel free to advance, explore and set their plan into motion on their own Ownership.
- Sharing - the success of one is the success of all, lessons should flow, each person can and should use the best practices from each other Cooperation
- When it comes to creative inspiration, job titles and hierarchy are meaningless. (Location 251)
- Often, finding a solution is a multi-step endeavor. There is the problem you know you are trying to solve—think of that as an oak tree—and then there are all the other problems—think of these as saplings—that sprouted from the acorns that fell around it. And these problems remain after you cut the oak tree down. (Location 280)
Chapter 2 - Pixar is Born
being a Giver is helpful in unexpected ways, mainly creating connections and reputation Mingling Weak Ties.
- When faced with a challenge, get smarter. (Location 533)
- Always take a chance on better, even if it seems threatening. (Location 539)
- it wasn’t enough for managers to have good ideas—they had to be able to engender support for those ideas among the people who’d be charged with employing them. (Location 656)
- For all the care you put into artistry, visual polish frequently doesn’t matter if you are getting the story right. (Location 747)
Chapter 3 - Defining Goal
Communication is more than just an "open door" policy, communication should flow beyond hierarchy, the lowest worker should be able to talk to high management, make their voice heard and affect the company, this will increase involvement and responsibility Proactiveness Freedom of speech
- The responsibility for finding and fixing problems should be assigned to every employee, from the most senior manager to the lowliest person (Location 929)
- You don’t have to ask permission to take responsibility. (Location 945)
- Being on the lookout for problems, I realized, was not the same as seeing problems. (Location 1132)
Chapter 4 - Pixar's Identity
investing in people is key to success, more than "the process" or smart ideas. People First. Good, divers teams will produce good ideas. Investing means more than just workers, but as people with a life, hobbies, family, homes. Trust the Process
- Getting the right people and the right chemistry is more important than getting the right idea. (Location 1306)
- it is the focus on people—their work habits, their talents, their values—that is absolutely central to any creative venture. (Location 1323)
- Find, develop, and support good people, and they in turn will find, develop, and own good ideas. (Location 1329)
- If we are in this for the long haul, we have to take care of ourselves, support healthy habits, and encourage our employees to have fulfilling lives outside of work. (Location 1349)
- excellence must be an earned word, attributed by others to us, not proclaimed by us about ourselves. (Location 1395)
Part 2 - Protecting the New
Chapter 5 - Honesty and Candor
Trust and Honesty are crucial for a healthy workplace. To promote honesty, we can create teams with psychological safety to speak up and open up. peer support. Keys for healthy communication:
- Small - teams should be small. Makes the interaction easier with less tension and social pressure. Start Small
- No authority - no one has "final say", all are considered equal peers
- Feedback - Focus on perspective and identifying problems, not offering solutions. The problem indicates nothing on the person. Feedback
- Collaboration - we work together for a shared goal and authentic desire to help each other. We are guided by constructive feedback, not ego.
- Time - it takes time to build trust
- Active listening - People should be actively listening to one another, trying to share their perspective and understand the other side Active Listening
Sharing ideas with others grants not only access to new skills, but mainly fresh perspective Clean Slate.
- Lack of candor, if unchecked, ultimately leads to dysfunctional environments. (Location 1457)
- Put smart, passionate people in a room together, charge them with identifying and solving problems, and encourage them to be candid with one another. (Location 1462)
- without the critical ingredient that is candor, there can be no trust. And without trust, creative collaboration is not possible. (Location 1469)
- The more people there are in the room, the more pressure there is to perform well. (Location 1506)
- We dare to attempt these stories, but we don’t get them right on the first pass. And this is as it should be. Creativity has to start somewhere, and we are true believers in the power of bracing, candid feedback and the iterative process—reworking, reworking, and reworking again, (Location 1517)
- The Braintrust’s notes, then, are intended to bring the true causes of problems to the surface—not to demand a specific remedy. (Location 1564)
- ideas—and thus films—only become great when they are challenged and tested. (Location 1567)
- You are not your idea, and if you identify too closely with your ideas, you will take offense when they are challenged. To set up a healthy feedback system, you must remove power dynamics from the equation—you must enable yourself, in other words, to focus on the problem, not the person. (Location 1574)
- A lively debate in a Braintrust meeting is not being waged in the hopes of any one person winning the day. To the extent there is “argument,” it seeks only to excavate the truth. (Location 1668)
- The Braintrust is valuable because it broadens your perspective, allowing you to peer—at least briefly—through others’ eyes. (Location 1703)
- A good note says what is wrong, what is missing, what isn’t clear, what makes no sense. A good note is offered at a timely moment, not too late to fix the problem. A good note doesn’t make demands; it doesn’t even have to include a proposed fix. (Location 1725)
- “There’s a difference between criticism and constructive criticism. With the latter, you’re constructing at the same time that you’re criticizing. You’re building as you’re breaking down, making new pieces to work with out of the stuff you’ve just ripped apart. That’s an art form in itself. (Location 1728)
- any successful feedback system is built on empathy, on the idea that we are all in this together, that we understand your pain because we’ve experienced it ourselves. (Location 1740)
- Seek out people who are willing to level with you, and when you find them, hold them close. (Location 1758)
- Safety leads to a better exchange of ideas. (Location 1817)
- the best feedback in a Braintrust meeting is feedback that gets the student to want to redo their homework. That’s very different than making them redo their homework. (Location 1863)
- “The blessing of having fresh eyes is that you have none of the baggage,” (Location 1901)
- You have to come in generous and open, bringing all your skills with you. And you have to leave your ego at the door.” (Location 1983)
Chapter 6 - Fear and Failure
Failure is an investment, an opportunity to learn and improve. Failure, but it is also (and always) painful. The worst thing you can do is to try and avoid it. When avoiding failures, you avoid risk, avoid trying new things, which is a recipe for decay. Risk Management Experimentation To be more open for failure and to reduce the pain of it:
- Share - Talk openly about your failures in a safe space
- set an example - be a role model for processing failure in a healthy way. Role Models
- Cultivate trust - it takes time, Authenticity and Consistency to create a feeling of trust, where its okay to fail, to develop a growth mindset. Trust
- Transparency - sharing problems, fears, doubts and failures with your team you make them part of the company, increasing ownership and comradery. Transparency
Like scientific experiments, every result, even "failed ones" are useful for progress, they indicate where you do need to go. Experimentation beats overplanning because failure is inevitable, so its better to "fail fast". Obstacles as stepping stones
Risk should be taken when the cost is low, i.e at the beginning of a project rather at the end, when it's more difficult and pricy. To reduce Attachment, and increase the chances for a clean slate, you can use Multitrack in your favor, working on multiple ideas simultaneously.
- Mistakes aren’t a necessary evil. They aren’t evil at all. They are an inevitable consequence of doing something new (and, as such, should be seen as valuable; without them, we’d have no originality). (Location 2023)
- To disentangle the good and the bad parts of failure, we have to recognize both the reality of the pain and the benefit of the resulting growth. (Location 2027)
- failure is a manifestation of learning and exploration. If you aren’t experiencing failure, then you are making a far worse mistake: You are being driven by the desire to avoid it. (Location 2039)
- In a fear-based, failure-averse culture, people will consciously or unconsciously avoid risk. They will seek instead to repeat something safe that’s been good enough in the past. Their work will be derivative, not innovative. (Location 2060)
- When experimentation is seen as necessary and productive, not as a frustrating waste of time, people will enjoy their work—even when it is confounding them. (Location 2102)
- any outcome is a good outcome, because it yields new information. If your experiment proved your initial theory wrong, better to know it sooner rather than later. (Location 2106)
- people who pour their energy into thinking about an approach and insisting that it is too early to act are wrong just as often as people who dive in and work quickly. The overplanners just take longer to be wrong (Location 2118)
- failure gives us chances to grow, and we ignore those chances at our own peril. (Location 2209)
- Our actions and behaviors, for better or worse, teach those who admire and look up to us how to govern their own lives. Are we thoughtful about how people learn and grow? As leaders, we should think of ourselves as teachers (Location 2252)
- Fear can be created quickly; trust can’t. Leaders must demonstrate their trustworthiness, over time, through their actions—and the best way to do that is by responding well to failure. (Location 2278)
- Be patient. Be authentic. And be consistent. The trust will come. (Location 2280)
- When you instantly resort to secrecy, you are telling people they can’t be trusted. When you are candid, you are telling people that you trust them and that there is nothing to fear. To confide in employees is to give them a sense of ownership over the information. (Location 2284)
- By sharing problems and sensitive issues with employees, we make them partners and part owners in our culture, and they do not want to let each other down. (Location 2289)
- A better measure of our success is to look at the people on our team and see how they are working together. Can they rally to solve key problems? If the answer is yes, you are managing well. (Location 2311)
- Rather than trying to prevent all errors, we should assume, as is almost always the case, that our people’s intentions are good and that they want to solve problems. Give them responsibility, let the mistakes happen, and let people fix them. (Location 2334)
- Management’s job is not to prevent risk but to build the ability to recover. (Location 2336)
- You can’t be creative without taking risks. (Location 2403)
Chapter 7 - the Hungry Beast and Ugly Baby
In each creative process you have two forces:
- The beast - the need to deliver finalized products, to make investments worthwhile, to bring efficiency into creativity, to know when to stop developing and investing because its beyond repair
- The baby - new creations are always bad at first First Batch Trash, they need time, attention, resources to become valuable, self sustaining.
When either side "wins", companies collapse, either because they no longer innovate (beast wins), or because they don't know When to Quit, Perfectionism and attachment takes over ("baby" wins). Therefore you must balance the two, which is tricky, and there' no "clear way" of doing it Balance Extremes
- when someone hatches an original idea, it may be ungainly and poorly defined, but it is also the opposite of established and entrenched—and that is precisely what is most exciting about it. (Location 2528)
- Making the process better, easier, and cheaper is an important aspiration, something we continually work on—but it is not the goal. Making something great is the goal. (Location 2569)
- When efficiency or consistency of workflow are not balanced by other equally strong countervailing forces, the result is that new ideas—our ugly babies—aren’t afforded the attention and protection they need to shine and mature. They are abandoned or never conceived of in the first place. (Location 2573)
- In a healthy culture, all constituencies recognize the importance of balancing competing desires—they want to be heard, but they don’t have to win. Their interaction with one another—the push and pull that occurs naturally when talented people are given clear goals—yields the balance we seek. (Location 2623)
Chapter 8 - Change and Randomness
We fear change because of:
- Uncertainty - whether the change will be good or not, how the new life would look like. Uncertainty is one of the deepest fears sense seeking creatures Uncertainty.
- Blindness - the "familiar" becomes so entrenched that we are blind to its flaws, so we are unaware of what needs change, and therefore we lack the motivation to do so Familiarity bias Change is essential for creativity and quality because of first batch trash.
Randomness in it's pure form is unpredictable, and is mixed as "Noise" in everyday events in various quantities, and hurts our ability to explain past events, and predict future ones. While we can retroactively learn from randomness to create more robust systems, we can't avoid it, and the failures it will bring Anti-Fragility .
Therefore we shouldn't Blame people when such mistakes occur, rather trust them to handle the situation and find a creative solution. Randomness can also be positive, and can attribute much to our success Luck. Which means we should be humble about our contribution to our success, and be aware that what worked in the past might not work again.
Change is easier to implement if we frame it as a "what if" when discussing, and as pilots Framing, When we "try it out". It makes people more open cognitively and emotionally less fearful. Reverse Thinking
- It’s folly to think you can avoid change, no matter how much you might want to. But also, to my mind, you shouldn’t want to. There is no growth or success without change. (Location 2741)
- it is precisely because of the inevitability of change that people fight to hold on to what they know. Unfortunately, we often have little ability to distinguish between what works and is worth hanging on to and what is holding us back and worth discarding. (Location 2764)
- Rather than fear randomness, I believe we can make choices to see it for what it is and to let it work for us. The unpredictable is the ground on which creativity occurs. (Location 2776)
- believe life should not be easy. We’re meant to push ourselves and try new things—which will definitely make us feel uncomfortable. (Location 2824)
- some people describe creativity as ‘unexpected connections between unrelated concepts or ideas.’ If that’s at all true, you have to be in a certain mindset to make those connections. So when I sense we’re getting nowhere, I just shut things down. We all go off to something else. Later, once the mood has shifted, I’ll attack the problem again.” (Location 2834)
- change is our friend because only from struggle does clarity emerge—makes (Location 2837)
- Self-interest guides opposition to change, but lack of self-awareness fuels it even more. Once you master any system, you typically become blind to its flaws; even if you can see them, they appear far too complex and intertwined to consider changing. (Location 2859)
- We can store patterns and conclusions in our heads, but we cannot store randomness itself. (Location 2883)
- Real patterns are mixed in with random events, so it is extraordinarily difficult for us to differentiate between chance and skill. (Location 2892)
- when it comes to randomness, our desire for simplicity can mislead us. Not everything is simple, and to try to force it to be is to misrepresent reality. (Location 2917)
- We need to be humble enough to recognize that unforeseen things can and do happen that are nobody’s fault. (Location 2967)
- If all our careful planning cannot prevent problems, then our best method of response is to enable employees at every level to own the problems and have the confidence to fix them. (Location 3006)
- Everyone says they want to hire excellent people, but in truth we don’t really know, at first, who will rise up to make a difference. (Location 3037)
- The existence of luck also reminds us that our activities are less repeatable. (Location 3054)
Chapter 9 - Hidden
We always have unknown unknowns, even if we have perfect knowledge in every human field, because the main unknown is humans. especially for managers, people would act, convey knowledge differently around you, and would avoid contacting you in critical situations out of fear or respect. All these can cause you to believe you know and see everything even when you're far from the truth.
More than that, we are all blind to others' perspective and experience. Theory of Mind. We see with our "mind", not our eyes, meaning that our brain "fills the gap" on what we expect to see, not what we actually see (and don't see). Even on hindsight, we are blind, seeing only our Subjective Reality, and we are blind to our own blindness. For example: Conformation Bias.
Miscommunication, misunderstanding, biases and ignorance can result from these mental models (aka mental glasses). Honesty, exploration and introspection are mechanisms against it
- If you don’t try to uncover what is unseen and understand its nature, you will be ill prepared to lead. (Location 3091)
- even if it were possible to learn every discipline and master every profession, we’d still have blind spots. That’s because there are other limitations—many of them rooted in the dynamics of human interaction—that keep us from having a clear picture of the world around us. (Location 3100)
- Here’s what turns a successful hierarchy into one that impedes progress: when too many people begin, subconsciously, to equate their own value and that of others with where they fall in the pecking order. Thus, they focus their energies on managing upward while treating people beneath them on the organizational chart poorly. (Location 3128)
- The leader’s view, then, is obstructed by these people who are skilled at figuring out what the leader wants. (Location 3138)
- There is nothing quite as effective, when it comes to shutting down alternative viewpoints, as being convinced you are right. (Location 3156)
- In a healthy, creative culture, the people in the trenches feel free to speak up and bring to light differing views that can help give us clarity. (Location 3161)
- to be truly humble, those leaders must first understand how many of the factors that shape their lives and businesses are—and will always be—out of sight. (Location 3210)
- Hindsight is not 20-20. Not even close. Our view of the past, in fact, is hardly clearer than our view of the future. While we know more about a past event than a future one, our understanding of the factors that shaped it is severely limited. (Location 3215)
- We are meaning-making creatures who read other people’s subtle clues just as they read ours. (Location 3247)
- We aren’t aware that the majority of what we think we see is actually our brain filling in the gaps. (Location 3253)
- We firmly believe that we are perceiving reality in its totality rather than a sliver of it. In other words, we are aware of the results of our brain’s processing but not the processing itself. (Location 3255)
- We have to learn, over and over again, that the perceptions and experiences of others are vastly different than our own. (Location 3270)
- If our mental models are mere approximations of reality, then, the conclusions we draw cannot help but be prone to error. (Location 3277)
- Our mental models aren’t reality. They are tools, like the models weather forecasters use to predict the weather. But, as we know all too well, sometimes the forecast says rain and, boom, the sun comes out. The tool is not reality. The key is knowing the difference. (Location 3298)
- But no matter how intensely we desire certainty, we should understand that whether because of our limits or randomness or future unknowable confluences of events, something will inevitably come, unbidden, through that door. Some of it will be uplifting and inspiring, and some of it will be disastrous. (Location 3320)
- Candor, safety, research, self-assessment, and protecting the new are all mechanisms we can use to confront the unknown and to keep the chaos and fear to a minimum. (Location 3334)
Part 3 - Building and Sustaining
Chapter 10 - Broadening Our View
To solve the difficulties that can arise from the existence of, and conflicting mental glasses, which are magnified as an organization grows, we use these techniques:
- Dailies - sessions where the explicit/declared goal is to share incomplete work, be open for suggestions, and putting ego at the door, so we could solve problems together and share viewpoints
- Research trips - go and explore new topics, physically if possible, gain experience knowledge, interview people who "live" this field, shadow them. To enrich your ability to create detailed, authentic, new creations. creativity isn't just a mixture of the familiar, you have to add something new.
- limits - Limits, if done right, can be seen as challenges and opportunities to explore new options, like achievements in video games Gamification, with the added benefit of the limit itself, which is usually to set resource or time constraints.
- Mixing tech and art - explore new tech that can expand your creativity
- Short experimentation - do small simulations to explore more deeply certain skills in a low-risk, low cost environment Simulations Pivot Chunking
- Learning to see - when faced with a problem, we need to learn to switch between the problems specific context, and it's archetype, so we could solve not only this problem, but others that stem from the same root Ripple effect.
- postmortem - useful for collecting and passing along lessons, solving communication issues. It forces self reflection, and prepare for the next project. Use data to support it, but don't rely solely on it because you can't measure everything. Be wary of it's structure, because each structure "forces" ways of thinking and answers. A basic frame is what to start/stop/continue doing. post-mortem
- Continue learning - learning sessions are not only useful socially - mingling people from different fields together in a light setting, but also it brings us back to Beginner's Mind, where we are open to new ideas, love learning in a non-judgmental way, like children, which is essential for creativity Lifelong Learning
- The intertwining of many views is an unavoidable part of any culture, and unless you are careful, the conflicts that arise can keep groups of people locked into their restrictive viewpoints even if, as is often the case, each member of the group is ordinarily open to better ideas. (Location 3444)
- As more people are added to any group, there is an inexorable drift toward inflexibility. (Location 3446)
- The first step is to teach them that everyone at Pixar shows incomplete work, and everyone is free to make suggestions. When they realize this, the embarrassment goes away—and when the embarrassment goes away, people become more creative. (Location 3499)
- Dailies are designed to promote everyone’s ability to be open to others, in the recognition that individual creativity is magnified by the people around you. The result: We see more clearly. (Location 3503)
- When filmmakers, industrial designers, software designers, or people in any other creative profession merely cut up and reassemble what has come before, it gives the illusion of creativity, but it is craft without art. Craft is what we are expected to know; art is the unexpected use of our craft. (Location 3519)
- You’ll never stumble upon the unexpected if you stick only to the familiar. (Location 3546)
- The very concept of a limit implies that you can’t do everything you want—so we must think of smarter ways to work. Let’s be honest: Many of us don’t make this kind of adjustment until we are required to. Limits force us to rethink how we are working and push us to new heights of creativity. (Location 3580)
- any time we impose limits or procedures, we should ask how they will aid in enabling people to respond creatively. (Location 3631)
- If we can constantly change and improve our models by using technology in the pursuit of art, we keep ourselves fresh. (Location 3651)
- when you embark on an experiment, you don’t know if you will achieve a breakthrough. Chances are, you won’t. But nevertheless, you may stumble on a piece of the puzzle along the way—a glimpse, if you will, into the unknown. (Location 3686)
- The goal is to learn to suspend, if only temporarily, the habits and impulses that obscure your vision. (Location 3779)
- Companies, like individuals, do not become exceptional by believing they are exceptional but by understanding the ways in which they aren’t exceptional. Postmortems are one route into that understanding. (Location 3793)
- In general, people are resistant to self-assessment. (Location 3812)
- By definition, postmortems are supposed to be about lessons learned, so if you repeat the same format, you tend to uncover the same lessons, which isn’t much help to anyone. (Location 3838)
- to soften the process is to ask everyone who is preparing for the postmortem to make two lists: the top five things that they would do again and the top five things that they wouldn’t do again. People find it easier to be candid if they balance the negative with the positive, and a good facilitator can make it easier for that balance to be struck. (Location 3847)
- If we think data alone provides answers, then we have misapplied the tool. It is important to get this right. Some people swing to the extremes of either having no interest in the data or believing that the facts of measurement alone should drive our management. Either extreme can lead to false conclusions. (Location 3863)
- Measure what you can, evaluate what you measure, and appreciate that you cannot measure the vast majority of what you do. (Location 3869)
- In the classroom setting, people interacted in a way they didn’t in the workplace. They felt free to be goofy, relaxed, open, vulnerable. Hierarchy did not apply, and as a result, communication thrived. Simply by providing an excuse for us all to toil side by side, (Location 3880)
- Creativity involves missteps and imperfections. I wanted our people to get comfortable with that idea—that both the organization and its members should be willing, at times, to operate on the edge. (Location 3884)
- The fear of judgment was hindering creativity. (Location 3898)
- it takes such discipline—some people even call it a practice—to turn off that inner critic in adulthood and return to a place of openness. (Location 3899)
- To have a “not know mind” is a goal of creative people. It means you are open to the new, just as children are. (Location 3901)
- By resisting the beginner’s mind, you make yourself more prone to repeat yourself than to create something new. The attempt to avoid failure, in other words, makes failure more likely. (Location 3907)
Chapter 11 - The Unmade Future
management is like sailing, you don't control everything, you will encounter storms, mirages, you don't even see your destination, but you have to confidently set a destination, prepare navigation systems Systematical Thinking and course correct along the way. Second, a manager needs to listen, and adapt to the situation and to people's views in order to find the best way to align their view to the company's, to create balance and synthesis Adaptability. Lastly, you need to be mindful, focus on the problem at hand, embrace the pain, not escape it. Know what you do and don't control, and put all other thoughts aside.
- creative people discover and realize their visions over time and through dedicated, protracted struggle. In that way, creativity is more like a marathon than a sprint. (Location 3920)
- to change the world, we must bring new things into being. (Location 3929)
- We humans like to know where we are headed, but creativity demands that we travel paths that lead to who-knows-where. (Location 3932)
- leadership is about making your best guess and hurrying up about it so if it’s wrong, there’s still time to change course. (Location 3993)
- sailing means that you can’t control the elements and that there will be good days and bad days and that, whatever comes, you will deal with it because your goal is to eventually get to the other side. You will not be able to control exactly how you get across. That’s the game you’ve decided to be in. If your goal is to make it easier and simpler, then don’t get in the boat.” (Location 3999)
- Instead of collapsing into a nervous mess, the director who has a clear internal model of what creativity is—and the discomfort it requires—finds it easier to trust that light will shine again. The key is to never stop moving forward. (Location 4014)
- Managing a multiplicity of forces, not to mention hundreds of people with minds of their own, requires balance. (Location 4061)
- there’s a fine balance between providing some structure and safety—financial and emotional—but also letting it get messy and stay messy for a while. To do that, you need to assess each situation to see what’s called for. And then you need to become what’s called for.” (Location 4068)
- Good producers—and good managers—don’t dictate from on high. They reach out, they listen, they wrangle, coax, and cajole. (Location 4074)
- Everything is changing. All the time. And you can’t stop it. And your attempts to stop it actually put you in a bad place. It causes pain, but we don’t seem to learn from it. Worse than that, resisting change robs you of your beginner’s mind—your openness to the new. (Location 4119)
- If you are mindful, you are able to focus on the problem at hand without getting caught up in plans or processes. Mindfulness helps us accept the fleeting and subjective nature of our thoughts, to make peace with what we cannot control. Most important, it allows us to remain open to new ideas and to deal with our problems (Location 4126)
Part 4 - Testing what We Know
Chapter 13 - Notes Day
Two methods of maintaining excitement in large old organizations are:
- Personal projects - two days a month a worker can spend his time freely, exploring new ideas that don't directly connect to his team/project
- Notes day - an open full day of suggestions and debates by employees on how to improve the company. It's important that hierarchy won't interrupt, and that people will be divided by interest, not role. Suggestions will need a volunteer to advocate and work on after Notes day has ended.
- fixing things is an ongoing, incremental process. Creative people must accept that challenges never cease, failure can’t be avoided, and “vision” is often an illusion. But they must also feel safe—always—to speak their minds. (Location 4788)
- the biggest payoff of Notes Day was that we made it safer for people to say what they thought. Notes Day made it okay to disagree. That and the feeling our people had that they were part of the solution were its biggest contributions. (Location 5027)
- Notes Day wasn’t an end point but a beginning—a way of making room for our employees to step forward and think about their role in our company’s future. (Location 5042)
- The truth is, as challenges emerge, mistakes will always be made, and our work is never done. We will always have problems, many of which are hidden from our view; we must work to uncover them and assess our own role in them, even if doing so means making ourselves uncomfortable; when we then come across a problem, we must marshal all our energies to solve it. (Location 5060)
- Unleashing creativity requires that we loosen the controls, accept risk, trust our colleagues, work to clear the path for them, and pay attention to anything that creates fear. Doing all these things won’t necessarily make the job of managing a creative culture easier. But ease isn’t the goal; excellence is. (Location 5063)
Chapter 15 - Incorporating Creativity
- instead of measuring where your work ends and the work of another begins, it is far better to ask: How do you connect with other people? How much have others added to the work you’ve done? And do we recognize and appreciate that we have built on what others have done? (Location 5841)
- I can never be another gender; I can never be another ethnicity; I can never be raised in another culture—there are experiences I can never have. But at the same time, I can have faith that people who are different from me have something of great value to add to whatever creative endeavor we are attempting together. (Location 5845)
- endorsing playfulness, I believe leaders also implicitly endorse self-expression. (Location 6150)
- The bravest thing a person can do is to accept their own limitations and fully embrace how much we all need one another. (Location 6205)